Example
To perform an ordinary exact match, only the first two arguments are required.
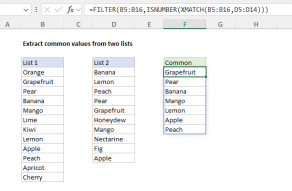
Typically, the XMATCH function is used together with the INDEX function to retrieve a valueat a specific location.
XMATCH vs.

MATCH
XMATCH is an upgraded replacement for the MATCH function.
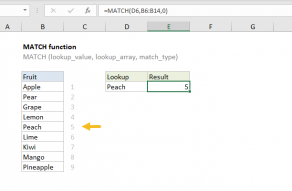
Like the MATCH function, XMATCH performs a lookup and returns a numeric position.
Let me know if you notice other differences and I will include them on this page.

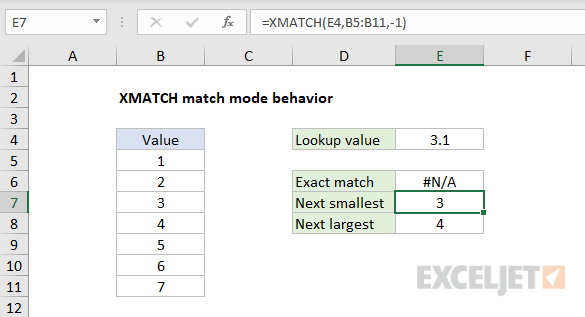
Note thatmatch_modeis an optional argument.
If you do not provide a value, XMATCH will default to an exact match.
TheXLOOKUP functionwas also updated to support regex.

For more about regex in Excel, seeRegular Expressions in Excel.
Search mode
The fourth argument for XMATCH issearch_mode.
If data is not sorted properly, a binary search can return invalid results that look perfectly normal.

XMATCH with wildcard
Whenmatch_modeis set to 2, XMATCH can perform a match usingwildcards.
Notice that XMATCH isnotcase-sensitive.
XMATCH with Regex
XMATCH can also match with “regex” (short for Regular Expressions).

This problem is trickier than it looks.
Each product code begins with 3 uppercase letters and ends with 2 or 3 uppercase letters.
In the middle of the product code is a number between 2 and 4 digits.
A wildcard match won’t work because a number like 56 can appear insideother product codes.
However, we can easily solve this problem with a “regex match”.
To enable a regex match in XMATCH, provide 3 formatch_mode.

Then supply a valid regex pattern as thelookup_value.
Regex is a powerful and somewhat complex language.
For a detailed explanation of the regex used in this example, seeXLOOKUP with regex.

XLOOKUP and XMATCH support regex in the same way.
Although the functions are different, the regex pattern is exactly the same.
Regex matching was added to XMATCH in December 2024, so this feature is only available in Excel 365.

For an introduction to regex in Excel, seeRegular Expressions in Excel.
For more details,see this page.
Case-sensitive match
The MATCH function is not case-sensitive.

This formula is explained in anINDEX and MATCH example here.
The example uses theMATCH function, but XMATCH can be substituted with the same result.
Binary search
XMATCH has a binary search option that runsvery quickly.

To enable binary search mode, data must be sorted in ascending or descending order.
If values are sorted inascending order, use the value 2 forsearch_mode.
If values are sorted indescending order, use the value -2.

XLOOKUP supports approximate and exact matching, wildcards (* ?)
MATCH supports approximate and exact matching, andwildcards(* ?)
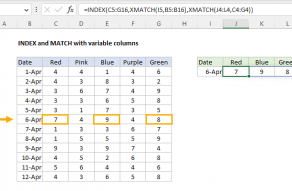
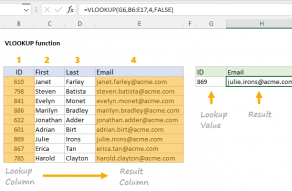
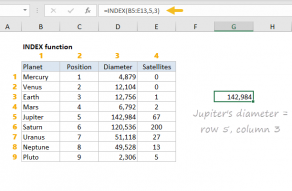
it’s possible for you to use INDEX to retrieve individual values, or entire rows and columns.

LOOKUP’s default behavior makes it useful for solving certain problems in Excel.
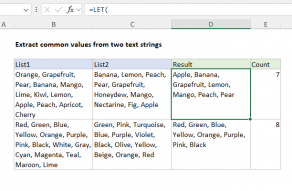
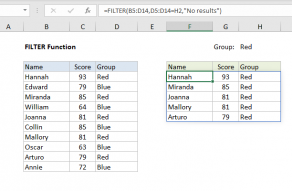
The output from FILTER is dynamic.
If source data or criteria change, FILTER will return a new set of results.

This makes FILTER a flexible way to isolate and inspect data without altering the…