Each approach is explained below.
January 1, 1900 is 1, January 2, 1900 is 2, and so on.
More recent dates are much larger numbers.

Because dates are just numbers, you could easily perform arithmetic on dates.
The SUMIFS function sums cells in arangethat meet one or more conditions, referred to ascriteria.
This is because the SUMIFS function is in a group ofeight functionsthat split logical criteria into two parts.

These are the first five dates in the data as shown.
Next, the array above is multiplied by the values in C5:C16.
With just one array to process, SUMPRODUCT returns the sum of all items in the array: 21,875.

Note: Why would you use SUMPRODUCT instead of SUMIFS?
The biggest reason is flexibility.
Unlike SUMPRODUCT, SUMIFSrequires a cell range; you could’t use an array.

This means SUMIFS won’t work informulas that need to manipulate valuesbefore conditional logic is applied.
The TODAY function takes no arguments.
it’s possible for you to format the value returned by TODAY with a datenumber format.

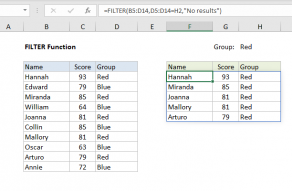
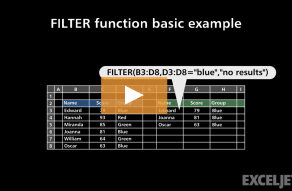
The output from FILTER is dynamic.
If source data or criteria change, FILTER will return a new set of results.