Explanation
Note: the core idea of this formula is adapted from an example inMike Girvin’sexcellent bookControl+Shift+Enter.
The example shown uses several formulas, which are described below.
This results in a two-dimensional array, 9 columns x 9 rows, filled with TRUE and FALSE values.

Thedouble negative(–) is used to coerce the TRUE FALSE values to 1s and zeros.
Otherwise, each cell will only show the first ranking value in the array that is returned.
If so, we assign a rank value that equals the row count in data.

This formula isexplained in detail here.
These formulas can be adapted toapply logical criteria, and SORT can be combined with UNIQUE.
The result from MMULT is anarraythat contains the same number of rows asarray1and the same number of columns asarray2.

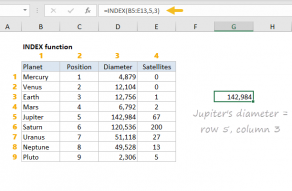
you’ve got the option to use INDEX to retrieve individual values, or entire rows and columns.
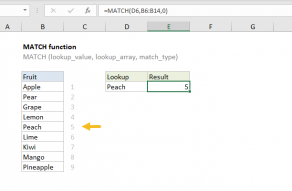
MATCH supports approximate and exact matching, andwildcards(* ?)