The first argument,text, is thetextstring to extract from.
This is typically a reference to a cell that contains text.
The second argument, callednum_chars, specifies the number of characters to extract.

Ifnum_charsis not provided, it defaults to 1.
Ifnum_charsis greater than the number of characters available, RIGHT returns theentiretext string.
The result is the two-letter abbreviation for the state.

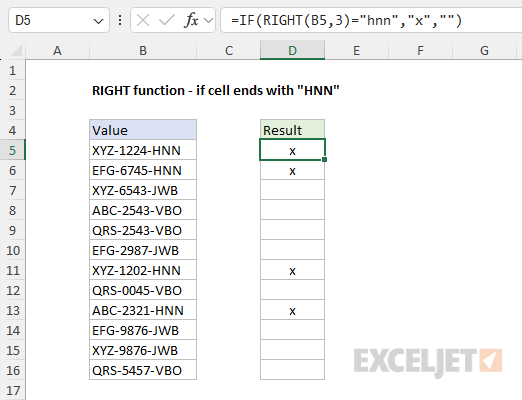
When the result is TRUE, IF returns “x”.
When the result is FALSE, IF returns an empty string “”.
The result is that the codes in column B that end with “abc” are clearly marked.

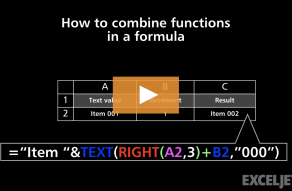
The screen below shows how this formula can be applied in a worksheet.
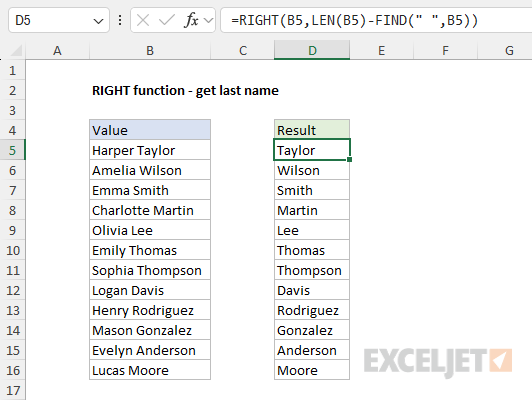
Next, the FIND function returns the position of the space character " " as a number.
The result from FIND is then subtracted from the result from LEN and returned to RIGHT as thenum_charsargument.

you’ve got the option to read a moredetailed explanation here.
Related functions
The RIGHT function is used to extract text from therightside of a text string.
Use theLEFT functionto extract text starting from theleftside of the text, and theMID functionto extract from themiddleof text.

For example, =LEFT(“apple”,3) returns “app”.
For example, =MID(“apple”,2,3) returns “ppl”.
LEN will also count characters in numbers, but number formatting is not included.

TEXTBEFORE Function
The Excel TEXTBEFORE function returns the text that occurs before a given substring or delimiter.
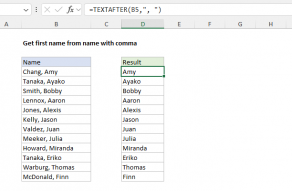
TEXTAFTER Function
The Excel TEXTAFTER function returns the text that occurs after a given substring or delimiter.
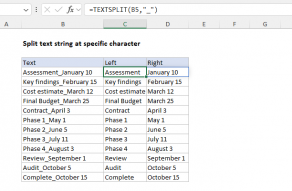
TEXTSPLIT can split text into rows or columns.