RANK.EQ works fine with sorted or unsorted data.
It is not necessary to sort the values in the list before using the RANK.EQ function.
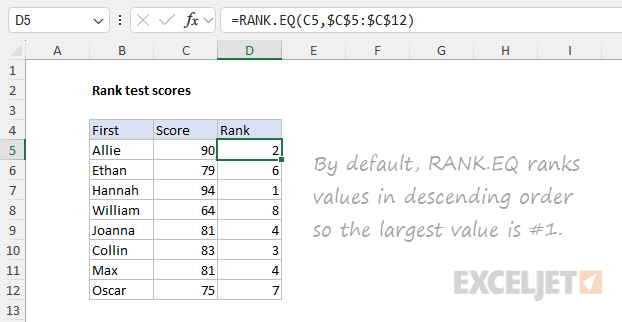
By default, RANK.EQ will rank values indescendingorder and assign 1 to thelargestvalue in the list.
However, this behavior can be reversed using the optionalorderargument as explained below.
RANK is still available for backward compatibility.
RANK.EQ and RANK are essentially the same function and there should be no cases where they return different results.

The optionalorderargument is not provided, since RANK.EQ will assign 1 to the largest value by default.
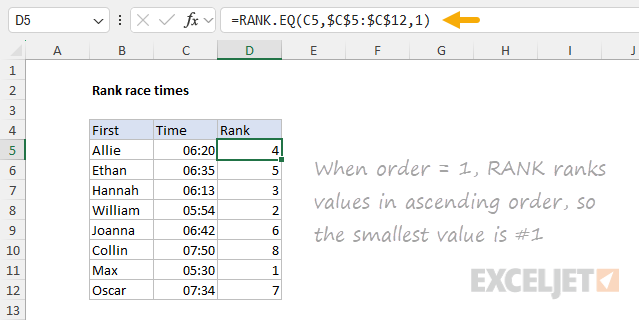
Also, note that the optionalorderargument is provided as 1 to force RANK.EQ to rank the times inascendingorder.
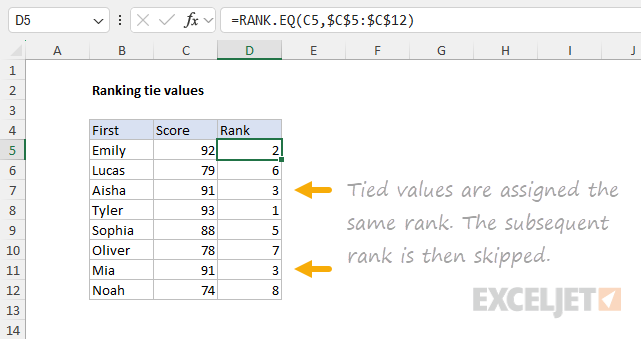
The next rank assigned will be 5, andno value will receive the rank of 4.

The RANK.EQ function assigns both a rank of 3 and the next rank, 4, is skipped.
If tied ranks are a problem, one workaround is to employ atie-breaking strategy.
RANK can rank values from largest to smallest (i.e.

top sales) as well as smallest to largest (i.e.
from a set of numeric data.