Explanation
In this example, the goal is to assign points based on a ranked score.
This is done by looking up the correct number of points to assign with INDEX and MATCH in thetblPointstable.
Because Katrina’s rank is 3, MATCH returns 3, which corresponds to row 3 intblPoints.

MATCH returns this position directly to theINDEX functionas therow_numargument.
The Points column oftblPointsis provided forarray:
INDEX returns 10 as the points awarded to Katrina.
The points for the remaining rows in the table are calculated in the same way.

See below for an adjustment to assign zero points to ranks after 6.
This will cause MATCH to return the #N/A error for any rank over 6.
The IFNA function “catches” this error when it occurs, and returns 0.
With theXLOOKUP function, the formula looks like this:
Note thematch_modeargument works a bit differently thanmatch_typein theMATCH function.
For exact match or next smaller, we need to use -1.
RANK can rank values from largest to smallest (i.e.
top sales) as well as smallest to largest (i.e.
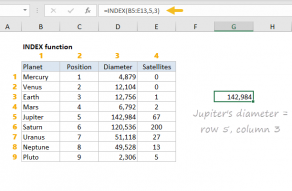
it’s possible for you to use INDEX to retrieve individual values, or entire rows and columns.
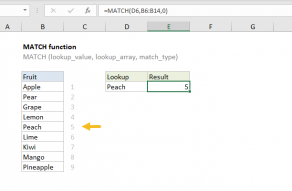
MATCH supports approximate and exact matching, andwildcards(* ?)
Often, MATCH is combined with the…