MID takes three arguments, all of which are required.
The firstargument,text, is the text string to start with.
The second argument,start_num, is the position of the first character to extract.
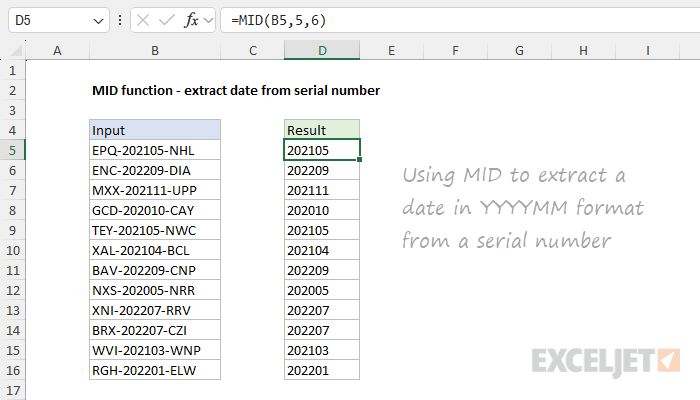
The third argument,num_chars, is the number of characters to extract.
Ifnum_charsis greater than the number of characters available, MID returns all remaining characters.
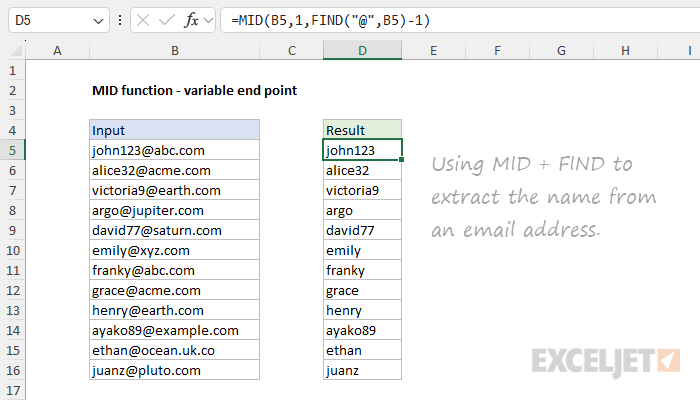
This can be done by combining MID with the FIND function.

We then subtract 1 and the result goes into the MID function as thenum_charsargument.
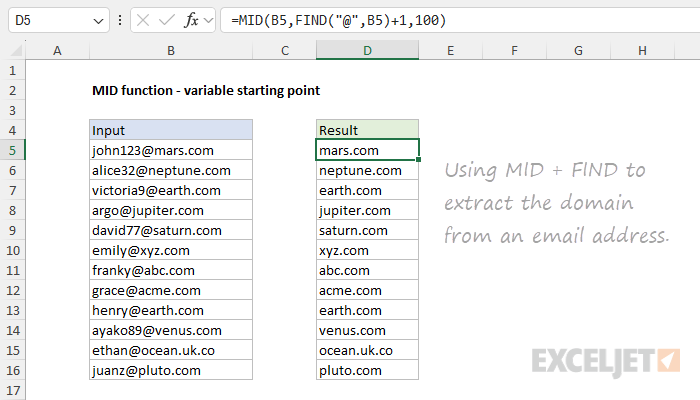
This too can be accomplished by combining MID with the FIND function.
In the worksheet below, the goal is to return the domain portion of each email address.

We then add 1 to the result from FIND to start at thenextcharacter.
Fornum_chars, we hardcode 100.
This is a simple hack.

Whennum_charsexceeds the characters that remain in a text string, MID returnsall remaining characters.
We take advantage of this behavior by providing an arbitrarily large number that will work in all cases.
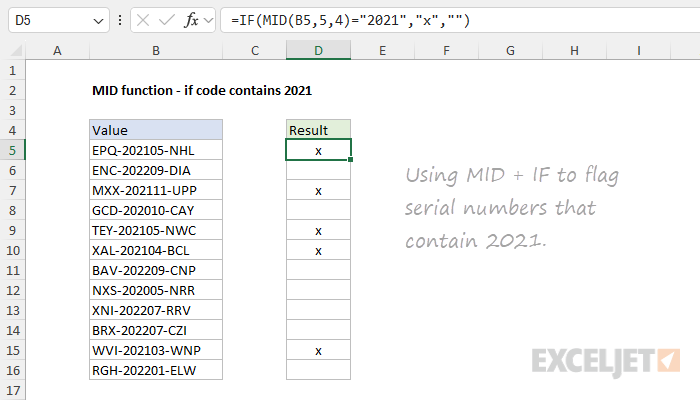
In the example below, a formula is used to flag serial numbers that contain “2021”.

The result is then compared to “2021” as the logical test inside the IF function.
When the result is TRUE, IF returns “x”.
Otherwise, IF returns an empty string ("").
The result is that serial numbers that contain “2021” are clearly identified.
The results is an array that contains all characters in the text string.
Seethis pagefor a full explanation.
Related functions
Use theMID functionto extract from themiddleof a text string.
TheLEN functionreturns the length of text as a count of characters.
UseFINDorSEARCHto locate an unknown starting or ending position.
For example, =LEFT(“apple”,3) returns “app”.
For example, =RIGHT(“apple”,3) returns “ple”.
For example, =MID(“apple”,2,3) returns “ppl”.

LEN will also count characters in numbers, but number formatting is not included.
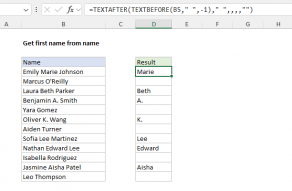
TEXTBEFORE Function
The Excel TEXTBEFORE function returns the text that occurs before a given substring or delimiter.
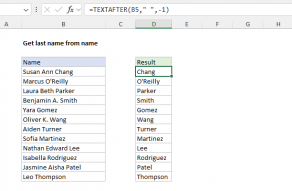
TEXTAFTER Function
The Excel TEXTAFTER function returns the text that occurs after a given substring or delimiter.

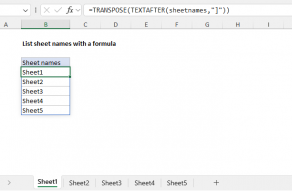
TEXTSPLIT can split text into rows or columns.