The set of birthdays are in anExcel Tablenameddatain the range B5:C29.
Thetdayvariable is defined with theTODAY function, which returns the current date.
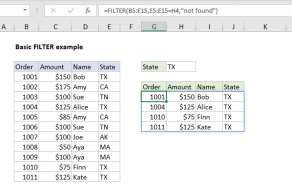
There are two challenges that we need to overcome to sort the birthdays like this.

From this date, the current date is subtracted.
The result is a count of days between the current date and the same date next year.
This is done to catch the 366 days that might occur in a leap year that includes February 29.
The result is an array of text values in the form “mmdd”.
So, for instance, the date November 2, 2021 becomes “1102”.
Notice the year value is simply discarded.
Inside theLET function, the result from TEXT is assigned to the variablecalendar.
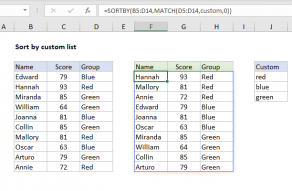
At this point, we have what we need to sort the list of birthdays.
The trick is we need to sort the birthdays by the order they will occur in the next year.
XMATCH performs an exact match by default, so no other arguments are required.
The result from SORTBY is assigned to the variablesorted.
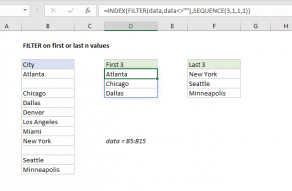
The last step is to slice off just the first 7 entries.

Forrow_numandcol_num, we use theSEQUENCE functionto create the arrays we need.
This prevents errors from appearing in the final output whennis larger than the total birthdays available in the table.
The range or array used to sort does not need to appear in results.
LET Function
The Excel LET function lets you define named variables in a formula.
in a text string with the number format of your choice.
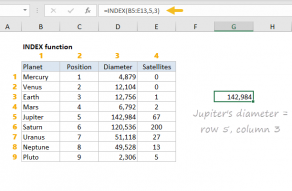
it’s possible for you to use INDEX to retrieve individual values, or entire rows and columns.

The array can be one dimensional, or two-dimensional, determined byrowsandcolumnsarguments.
It is a more robust and flexible successor to the MATCH function.
XMATCH supports approximate and exact matching, reverse search, and wildcards (* ?)

…
Related videos
The SEQUENCE function
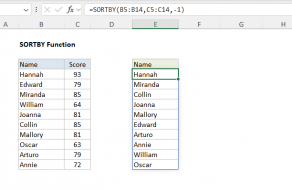
Basic SORTBY function example