Once defined and named, a LAMBDA function can be used anywhere in a workbook.
LAMBDA functions can be very simple or quite complex, stringing together many Excel functions into one formula.
A custom LAMBDA function does not require VBA or macros.

An anonymous function is a function defined without a name.
In Excel, the LAMBDA function is first used to create a generic (unnamed) formula.
TheLET functionis often used together with the LAMBDA function.

LET provides a way to declare variables and assign values in a formula.
This makes more complicated formulas easier to read by reducing redundant code.
The LET function can also improve performance by reducing the number of calculations performed by a formula.

By default, all arguments in a LAMBDA function are required.
To createoptionalarguments, see theISOMITTED function.
The first thing to consider is if the formula requires inputs (parameters).

This allows the formula to be tested directly on the worksheet before the LAMBDA is named.
First, copy the formula,but do not includethe testing parameters at the end.
Next, kick off the Name Manager with the shortcutControl + F3, and click New.

(Tip: Use the tab key to navigate to the “Refers to” field).
check that the formula begins with an equals sign (=).
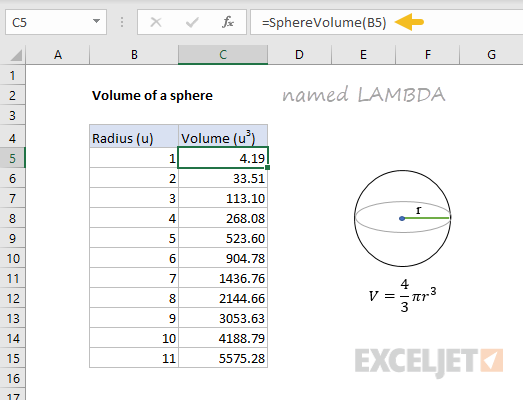
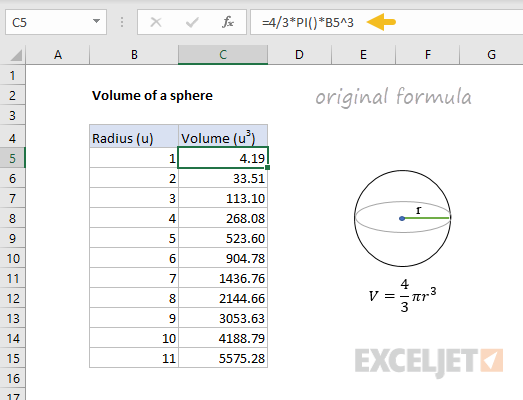
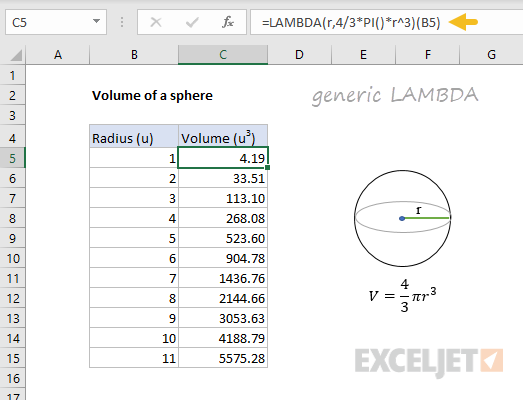
The generalExcel formula for calculating the volume of a sphereis:
where A1 represents the radius.

The name used for a LAMBDA function can be any valid Excel name.
In this case, we’ll name the formula “SphereVolume”.
We’ll address this problem below.

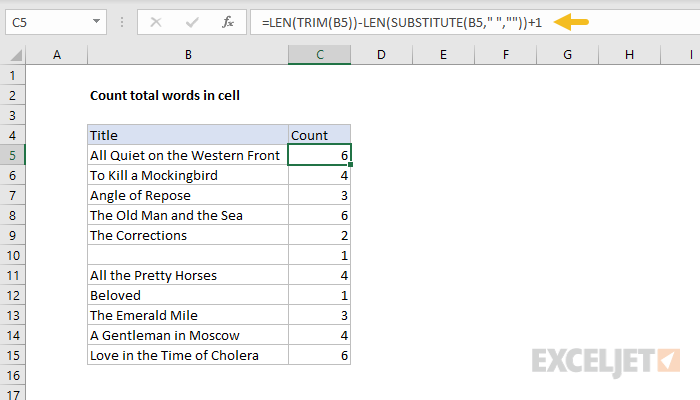
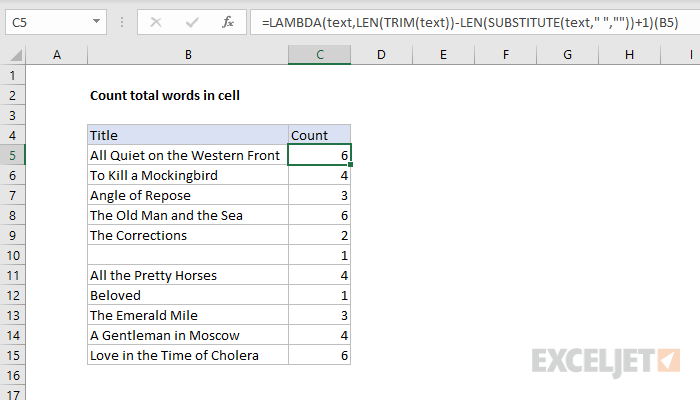
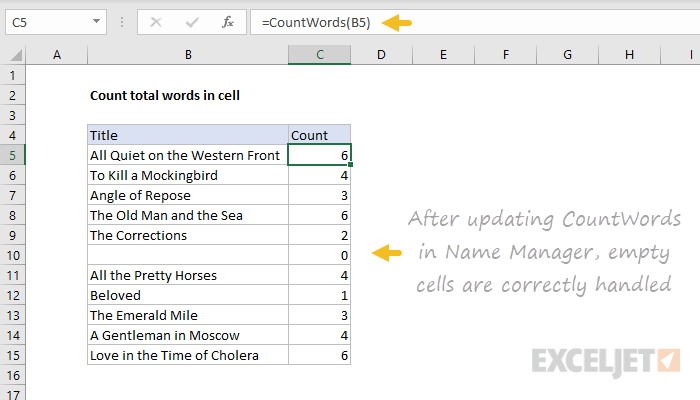
This formula only requires one input: the text containing words.
In our LAMBDA function, we’ll name this argument “text”.
In the screen below, we’ve replaced the original formula with the generic LAMBDA version.

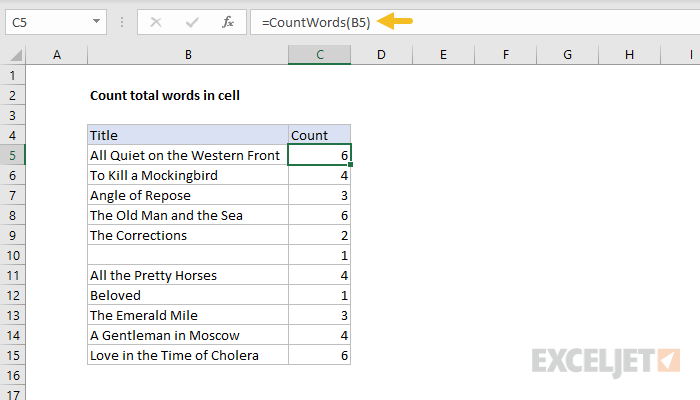
We’ll name this formula “CountWords”.
Notice we get exactly the same results.
This problem can be fixed by replacing +1 with the code below:
Full explanation here.

This is a key benefit of custom functions created with LAMBDA formula updates can be managed in one place.
The result can be very confusing.
Avoid this trouble by making sure your custom function name is unique.
LET Function
The Excel LET function lets you define named variables in a formula.
Inside a LAMBDA function, ISOMITTED will return TRUE when an argument has not been provided.
BYCOL can apply stock functions like SUM, COUNT, and AVERAGE or a custom LAMBDA function.
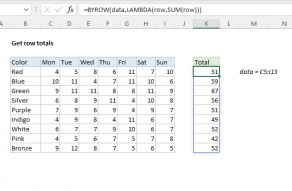
BYROW can apply stock functions like SUM, COUNT, and AVERAGE or a custom LAMBDA function.
All results are returned at the same time in a single array….