The article below first reviews how taxes are computed in a progressive system.
New: I’ve updated the worksheet to include tax rates for the year 2024.
The more you earn, the more income falls into higher brackets, which have a progressively higher rate.
The IRSpublishes brackets and tax rateseach year.
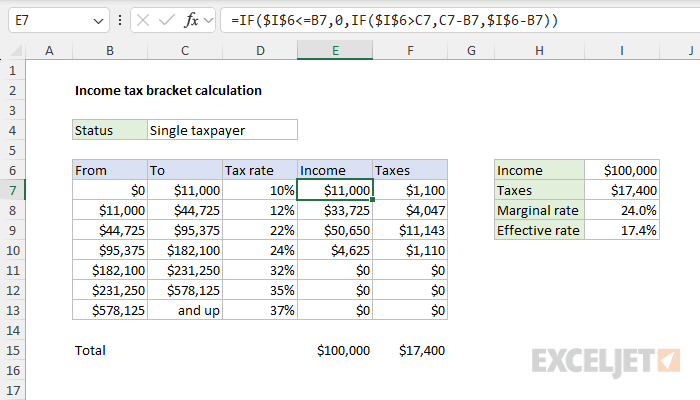
The marginal tax rate is 22%, and the effective tax rate is 17.1%.
Let’s solve this problem in a fun, modern way.

The hard part of this problem is splitting the income by bracket.
These are the numbers seen in the range E7:E13.
To be clear, the math is simple, but implementing the math using cell references can be tricky.

Next, we get to the heart of the formula, which is based on a nestedIF function.
This is a good approach because it makes it easy to validate results at any point.
But what if you want to calculate the total taxes owed in asingleformula?

In that case, we need to add a few more lines of code to our formula.
Next, let’s look at how to calculate the marginal and effective tax rates.
Marginal vs. Themarginal taxis the tax rate applied to the last dollar earned.

Theeffective taxis the overall percentage of income paid in taxes.
The lookup formulas below are advanced.
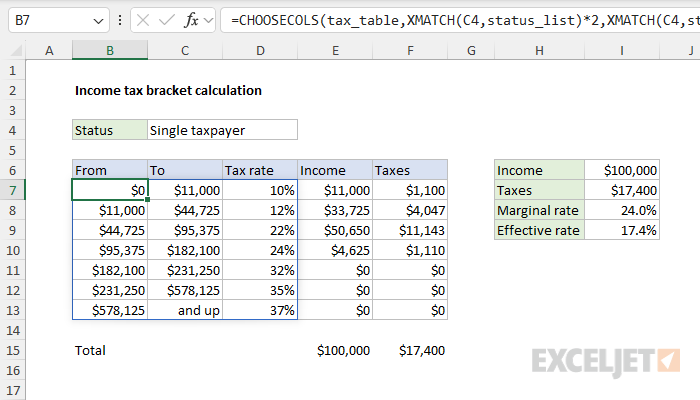
For example, “Married filing jointly” is item 2 in the list of status options.

Specifically, we want to retrieve columns 4 and 5 when the filing status is 2.
The trick is working out the simple math operations needed to convert the 2 into a 4 and 5.
If you haven’t been exposed to this idea before, don’t be discouraged.
Learning how to design and implement formulas like this takes time and practice.
Seethis pagefor a simplified example with a more detailed explanation.
The formulas explained above split income into brackets and apply the correct tax rates.

However, we still need to adapt the worksheet to make the tax rates reflect user choices.
This is an advanced lookup scenario, and it requires careful design.
The goal is to dynamically retrieve the correct tax rate data based on the selected year and filing status.

This table contains ten columns in total.
The first column contains the tax rate brackets.
The next eight columns contain the thresholds for each filing status.
The last column is Year, which contains the year the brackets were active.
There are seven brackets, so seven rows for each year.
Back on Sheet1, cell C4 contains a dropdown list that presents values from thestatus_list.

Cell F4 is a similar dropdown list that lets the user grab the year fromyear_list.
Both dropdowns are created withData Validation.
The result from FILTER is the subset of the tax rates that correspond to the year in F4.

This is delivered directly to the outer CHOOSECOLS function as thearrayargument.
When the status is “Single taxpayer”, the first XMATCH returns 2 and the second returns 3.
Putting the 1 last also effectively reorders the columns as needed, knocking off Step 3 from above.

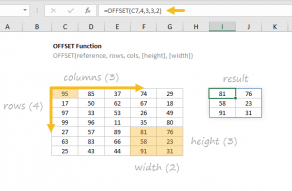
One alternative is to use theOFFSET functionwith theMATCH function.
This formula extracts a 7-row by 2-column range from thetax_tablebased on the taxpayer status and year selected.
The tricky part is calculating the right offsets for the selected year and status.

If F4 = 2023, MATCH returns 2 (since 2023 is in the second row).
We handle the rows offset in the same way as above.
Then, we provide 0 for the column offset to get to get column 1.

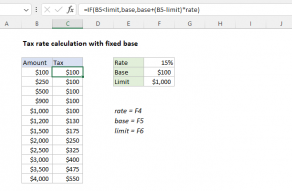
More than one condition can be tested by nesting IF functions.
The IF…
LET Function
The Excel LET function lets you define named variables in a formula.
The number of rows and columns to remove is provided by separaterowsandcolumnsarguments.

XLOOKUP supports approximate and exact matching, wildcards (* ?)
It is a more robust and flexible successor to the MATCH function.
XMATCH supports approximate and exact matching, reverse search, and wildcards (* ?)

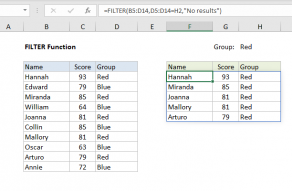
The output from FILTER is dynamic.
If source data or criteria change, FILTER will return a new set of results.
OFFSET is handy in formulas that require a dynamic range.

CHOOSECOLS Function
The Excel CHOOSECOLS function returns specific columns from an array or range.
The columns to return are provided as numbers in separate arguments.
Each number corresponds to the numeric index of a column in the given array.
Related videos
What are Dynamic Array formulas?
Dynamic arrays are native