This is a pretty simple problem in the latest version of Excel, which provides theTEXTBEFORE function.
In older versions of Excel, you might use a more complicated formula based on theLEFTandFINDfunctions.
Both options use theCELL functionto get a full path to the current workbook.

Read below for a full explanation.
If you have the latest version of Excel, you should use a formula based on the TEXTBEFORE function.
Otherwise, it’s possible for you to use the LEFT and FIND functions as explained below.

The CELL function is nested inside the TEXTBEFORE function, which is nested inside the SUBSTITUTE function.
CELL is avolatile functionand can cause performance problems in larger or more complicated worksheets.
The cell reference is arbitrary and can be any cell in the worksheet.

We subtract 1 because we want to remove textstarting withthe “]” that follows the filename.
This number is returned directly to theLEFT functionas thenum_charsargument.
Thetextargument is again provided by theCELL function:
TheLEFT functionreturns the first 26 characters oftext.

The pop in of information to be returned is specified asinfo_type.
For example, =LEFT(“apple”,3) returns “app”.
When the text is not found, FIND returns a #VALUE error.
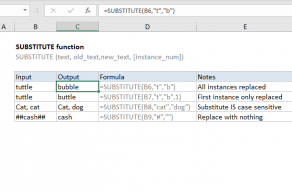
SUBSTITUTE Function
The Excel SUBSTITUTE function replaces text in a given string by matching.
