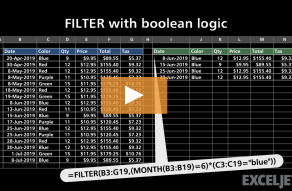
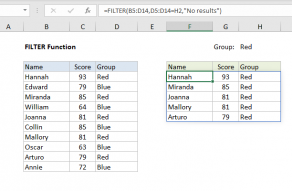
The conditions are provided as logical expressions that test the source data and return TRUE or FALSE.
The result from FILTER is anarrayof matching values from the original data.
The results from FILTER aredynamic.
If source data changes, or if conditions are modified, FILTER will return new results.
This makes FILTER a very good way to isolate and inspect specific data without altering the original dataset.
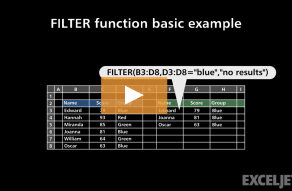
Basic example
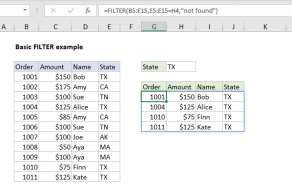
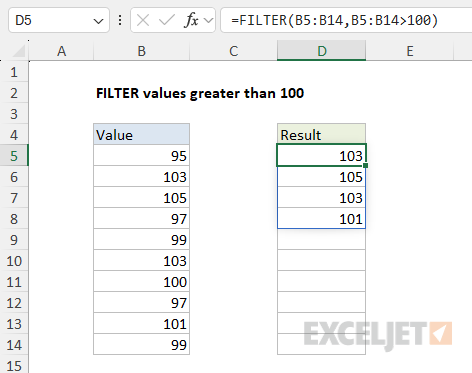
The FILTER function takes two required arguments:arrayandinclude.

The arrayis the source data to filter.
Theincludeargument should consist of one or morelogical teststhat return TRUE or FALSE.
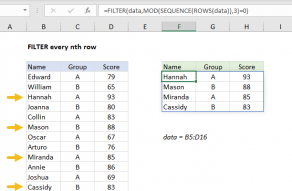
The FILTER function uses this array to “filter” the values in B5:B14.

All matching records are returned to the worksheet starting from cell F5, where the formula resides.
Values can be hardcoded as well.
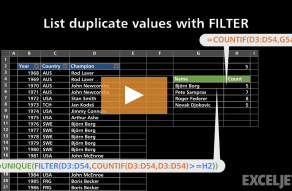
Often,is_emptyis configured to provide a message to the user.

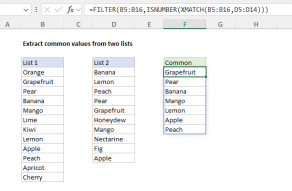
TheISNUMBER functionis used to convert the result from SEARCH into TRUE or FALSE.Read a full explanation here.
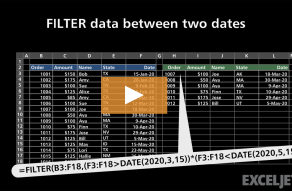
Filter by date
FILTER can be used with dates by constructing logical tests appropriate forExcel dates.
See this page for a full explanation.

See below for more examples.
Wildcards
The FILTER functiondoes notsupport thewildcards(*?~) like the XLOOKUP function.
SeeFILTER text containsandCell contains specific textfor a more complete explanation.
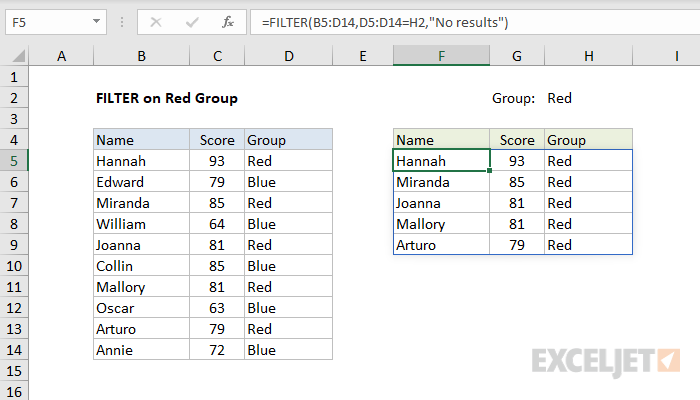
The output from FILTER is dynamic.
If source data or criteria change, FILTER will return a new set of results.
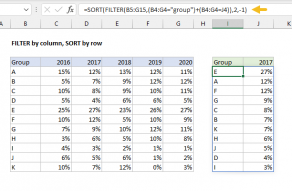
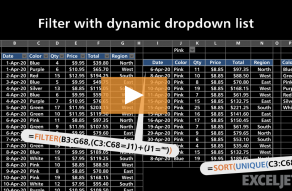
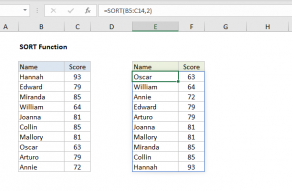
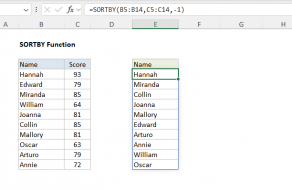
Values can be sorted by one or more columns.

SORT returns a dynamic array of results.
The range or array used to sort does not need to appear in results.
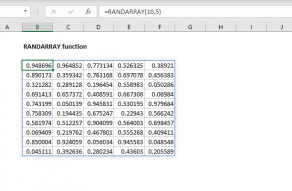
RANDARRAY Function
The Excel RANDARRAY function generates an array of random numbers between two values.

The size or the array is specified byrowsandcolumnsarguments.
The generated values can be either decimals or whole numbers.
SEQUENCE Function
The Excel SEQUENCE function generates a list of sequential numbers in an array.

The array can be one dimensional, or two-dimensional, determined byrowsandcolumnsarguments.