This is a bit sloppy, but it avoids having to calculate the exact number of characters to extract.
Next, to extract just the word we want (i.e.
@word), we use LEFT to extract the first 100 characters from the left.

This gets us “@word”, plus many extra spaces.
For that, we use the TRIM function.
Note: 100 represents the longest word you expect to find that begins with the special character.
Increase or decrease to suit your needs.
For example, =MID(“apple”,2,3) returns “ppl”.
LEN will also count characters in numbers, but number formatting is not included.
When the text is not found, FIND returns a #VALUE error.
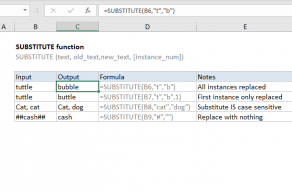
SUBSTITUTE Function
The Excel SUBSTITUTE function replaces text in a given string by matching.
For example, =REPT(“x”,5) returns “xxxxx”.