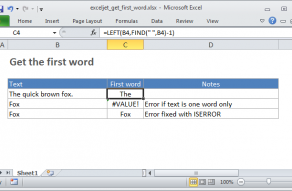
The article below explains two approaches.
See below for details.
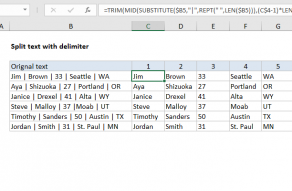
TEXTSPLIT function
The TEXTSPLIT function provides a simple way to solve this problem.
As the name implies, TEXTSPLIT will split text into pieces using a custom delimiter.
Thecol_delimiterargument is provided as a single space (" “).
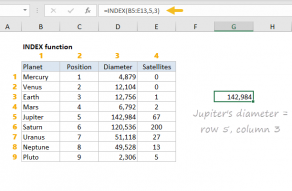
The array is returned directly to theINDEX functionas thearrayargument.

Therow_numargument is provided as a reference to cell C5.
Removing extra space
The operation of this formula depends on there being asinglespace between each word.
If there is the possibility of more than one space between words, the formula may return incorrect results.

The resulting text is then passed into the TEXTSPLIT function as before.
This ensures that the results from TEXTSPLIT will be consistent.
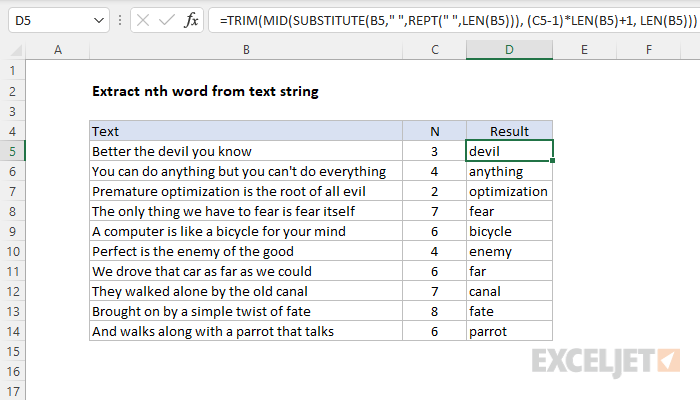
Then it splits the text string between words and cleans up the result with theTRIM function.

The formula uses theMID functionto extract the nth word.
We are just repeating the logic used previously to calculate the number of spaces to use between words.
The n-1 adjustment is needed because the extra space occursbetweenwords, i.e.

With this information, the MID function extracts 25 characters, beginning with character 51.
TEXTSPLIT can split text into rows or columns.
you’ve got the option to use INDEX to retrieve individual values, or entire rows and columns.
For example, =MID(“apple”,2,3) returns “ppl”.
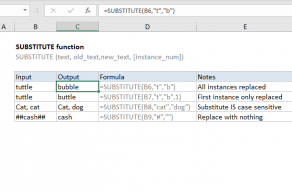
SUBSTITUTE Function
The Excel SUBSTITUTE function replaces text in a given string by matching.
For example, =REPT(“x”,5) returns “xxxxx”.

LEN will also count characters in numbers, but number formatting is not included.