The challenge is to determine the starting position, which is just after the second to last space.
The clever work is done primarily with the SUBSTITUTE function, which has an optional argument called instance number.
In the example shown, there are 5 spaces in the text, so the code above returns 4.
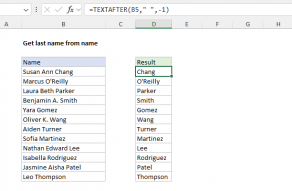
The choice of @ is arbitrary.
you might use any character that will not appear in the original text.
This is the starting position, and goes into the MID function as the second argument.
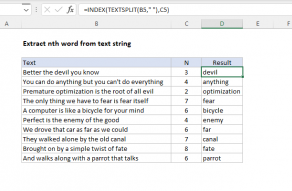
For simplicity, the number of characters to extract is hardcoded as 100.
This number is arbitrary and can be adjusted to fit the situation.
For example, =MID(“apple”,2,3) returns “ppl”.

LEN will also count characters in numbers, but number formatting is not included.
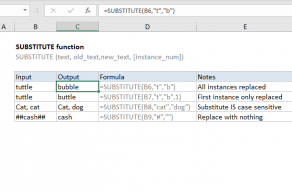
SUBSTITUTE Function
The Excel SUBSTITUTE function replaces text in a given string by matching.
When the text is not found, FIND returns a #VALUE error.