The position of the date is not known, so the date must be located as a first step.
MID is designed to extract a given number of characters from the middle of a text string.
SEARCH will return the position of a matching value as a number.
“, and the within_text is provided as B5.
The SEARCH supports wildcards, and the “?”
character meansany single character.

The pattern “??/??/??”
The text in cell B5 is 57 characters long, and the date begins at character 37.
The SEARCH function finds the date pattern and returns 37 as a result.

This result lands inside the MID function as thestart_num.
We use 8 because a date in the format “mm/dd/yy” is eight characters.
This is a simple hack to get a valid date from a text string.

In this case, Excel recognizes that “06/15/24” as a date and performs the conversion.
We can apply this formatting because we have converted text value into a valid Excel date.
This format can be adjusted to display dates as desired.

Although this formula is fairly simple, it is not especially robust.
For example, it will match the non-date “AA/BB/CC” and even “AAAA/BB/CCCC”.
(2) This formula works because theSEARCH functionsupports wildcards, unlike theFIND function.

Compared to the MID + SEARCH formula above, this formula does a better job of matching dates.
It is more flexible in some ways but more restrictive in others.
It also doesn’t validate the year in any way.

It would, for example, allow a 3-digit year, which Excel won’t interpret correctly.
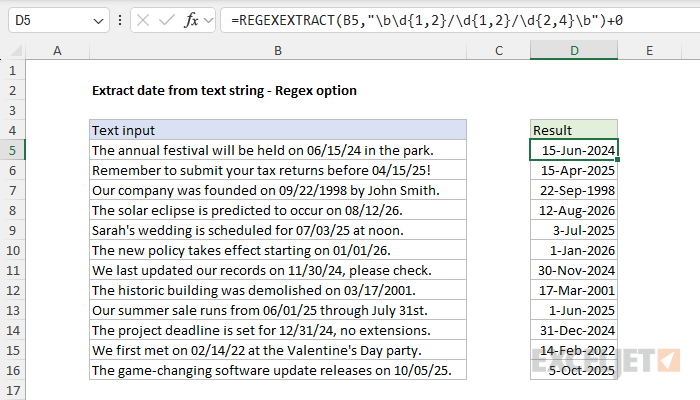
Since this is regex, we can easily make the pattern more specific.
REGEXEXTRACT is ahuge upgradeto Excel’s tools for matching and extracting text.

For example, =MID(“apple”,2,3) returns “ppl”.
SEARCH Function
The Excel SEARCH function returns the location of one text string inside another.
SEARCH returns the position offind_textinsidewithin_textas a number.

By default, REGEXEXTRACT will return the first match, but…


