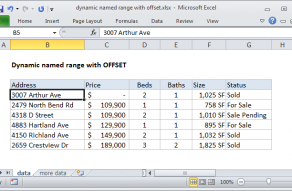
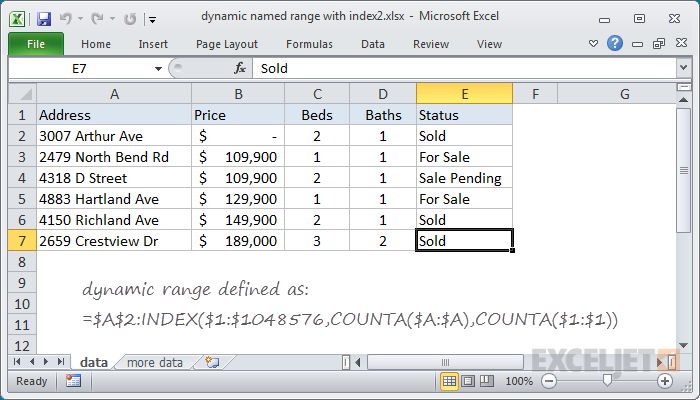
Dynamic named ranges automatically expand and contract when data is added or removed.
They are an alternative to using anExcel Table, which also resizes as data is added or removed.
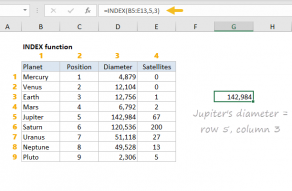
TheINDEX functionreturns the value at a given position in a range or array.
What makes INDEX especially useful for dynamic named ranges is that it actually returns a reference.
This means you could use INDEX to construct amixed referencelike $A$1:A100.
COUNTA works well here because there are 10 values in column A, including a header row.

COUNTA therefore returns 10, which goes directly into INDEX as the row number.
These are supplied to INDEX as row_num and column_num respectively.
you’re free to use INDEX to retrieve individual values, or entire rows and columns.

COUNTA does not count empty cells.
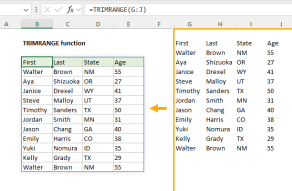
TRIMRANGE Function
The Excel TRIMRANGE function removes empty rows and columns from a range of data.
The result is a “trimmed” range that only includes data from the used portion of the range.