It also explains how to convert values in place with Paste Special, which does not require a formula.
The problem
Sometimes Excel will incorrectly evaluate a number as a text value.
One way to understand how Excel is interpreting a value is to check the alignment.

Alignment can be changed, however, so this is not a foolproof method of checking values.
Another way to check for numbers is to sum the values with the SUM function.
you could also test values more explicitly with the ISNUMBER function or the ISTEXT function.
a number, date, or time format) into a numeric value.
If the conversion succeeds, a number will be returned.
If the conversion fails, the result will be a #VALUE error.

This approach leaves the converted values in the same cells.
The basic steps are as follows:
Video:How to perform in-place changes with Paste Special.
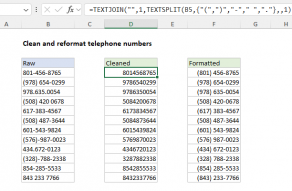
For more complicated situations, the best option is usually to remove all non-numeric characters before attempting a conversion.

For details, seeStrip non-numeric characters.
a number, date, or time format) into a numeric value.
Normally, the VALUE function is not needed in Excel, because Excel automatically converts text to numeric values.

For example, =LEFT(“apple”,3) returns “app”.
For example, =RIGHT(“apple”,3) returns “ple”.