The article below explains two approaches.
One approach is based on theAVERAGEIFS function, which is designed to calculate averages using multiple criteria.
The second approach is based on theFILTER functionand theAVERAGE function.

See below for more information.
Notice we need toconcatenatethe dates tological operators, as required by the AVERAGEIFS function.
Using EDATE is a simpler and more robust solution.

As you’ve got the option to see, only the first date occurs in January 2022.
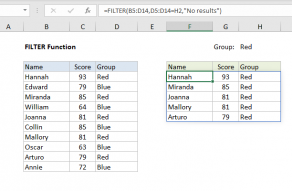
The FILTER function uses this array to select only values indatathat meet criteria.
The result is delivered directly to the AVERAGE function like this:
AVERAGE then returns a result of 100.

This is because the logic created with the TEXT function only compares month and year values.
For a side-by-side comparison of formulas vs. pivot tables, see this video:Why pivot tables.
The output from FILTER is dynamic.

If source data or criteria change, FILTER will return a new set of results.
Related videos
How to use the AVERAGEIFS function
FILTER function basic example