When you want to pull information from a table, the Excel VLOOKUP function is a great solution.
And yet, although VLOOKUP is relatively easy to use, there is plenty that can go wrong.
Which you probably aren’t.

This can cause results thatlook completely normal, even though they aretotally incorrect.
How VLOOKUP works
VLOOKUP is a function to look up and retrieve data in a table.
(For horizontally structured data, seeHLOOKUP).

VLOOKUP requires that the table be structured so that lookup values appear in the left-most column.
The data you want to retrieve (result values) can appear in any column to the right.
When you use VLOOKUP, imagine that every column in the table is numbered, starting from the left.

You’ll also have to supply a smaller table to VLOOKUP that starts with the lookup column.
you’re free to overcome this limitation by using INDEX and MATCH instead of VLOOKUP.
To VLOOKUP, a product code like “PQRF” is identical to “pqrf”.

VLOOKUP has two matching modes
VLOOKUP has two modes of operation: exact match and approximate match.
In most cases, you’ll probably want to use VLOOKUP in exact match mode.
In these cases, you likely won’t find the exact lookup value in the table.

Instead, you want VLOOKUP to get you the best match for a given lookup value.
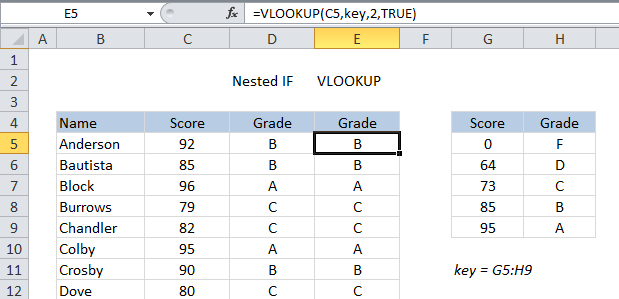
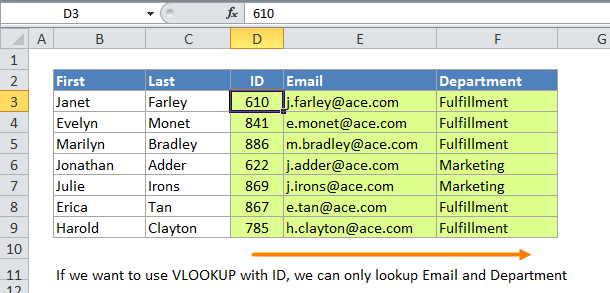
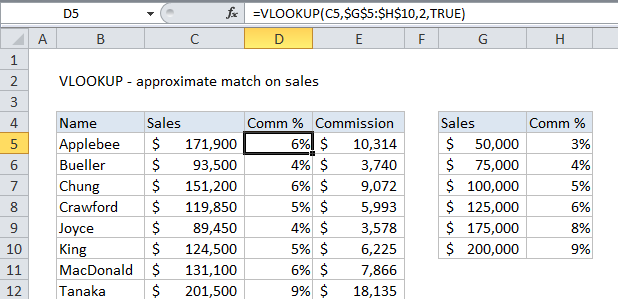
The formula in D5 does an approximate match to retrieve the correct commission:
6.
This name is not intuitive, so you’ll just have to memorize how it works.
For an exact match, use FALSE or 0.
When doing an approximate match, VLOOKUP assumes the table is sorted and performs a binary search.
This is a clear indication that the value isn’t found in the table.

That way, you always have a visual reminder of the match mode you expect.
Video:How to use VLOOKUP for approximate matches
9.
Otherwise, you may getincorrect results.

Also be aware that sometimes text data maylooksorted, even though it’s not.
Felienne Hermanshas a great example of this problem here, from a cool analysis she did on actualEnronspreadsheets!
In the example below, we are using two VLOOKUP formulas.

One to pull in the customer name, and the other to pull in the customer state.
Link:Example of merging with VLOOKUP.
Video:How to use VLOOKUP to merge tables.
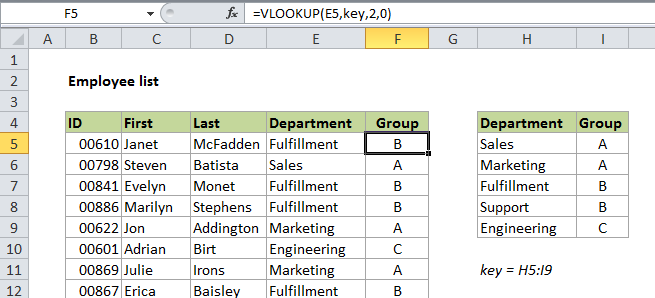
But you could also use VLOOKUP to assign arbitrary categories.
This is because hard-coded column index values don’t change automatically when columns are inserted or deleted.
The formula we are using is this:
16.

This is sometimes called a two-way lookup since you are looking up both the row and the column.
The trick is to use the MATCH function in place of a static column index.
See how in this quick video:How to do a two-way lookup with INDEX and MATCH.

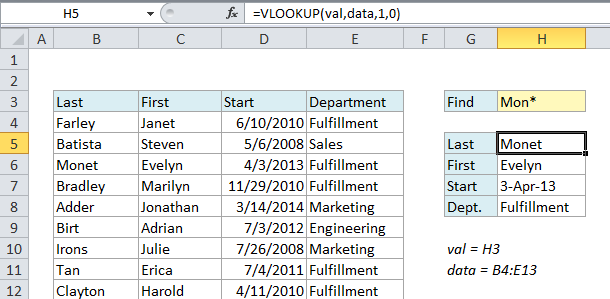
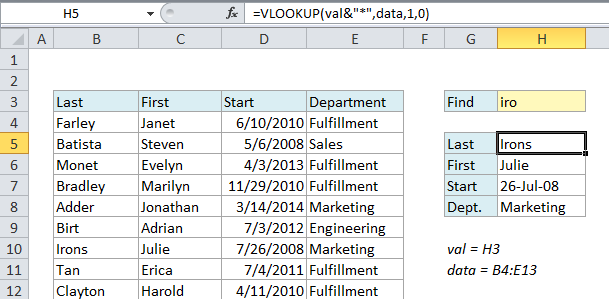
This causes VLOOKUP to match the name “Monet”.
This is a useful error because VLOOKUP is telling you clearly that it can’t find thelookup_value.
The easiest way to trap errors with VLOOKUP is to wrap VLOOKUP in the IFERROR function.

IFERROR allows you to “catch” any error and return a result of your choosing.
Here is the formula:
19.
If you are simply retrieving numbers as text from a column in a table, it doesn’t matter.
One way to do this is to convert the values in the lookup column to numbers.
An easy way to do this is toadd zero using paste special.
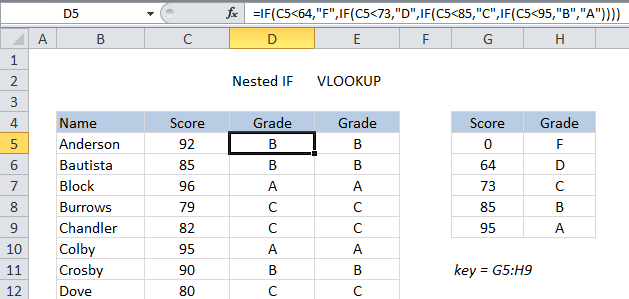
By contrast, VLOOKUP can assign the same grades with a simple formula.

All you better do is double-check the grade key table is set up for VLOOKUP (i.e.
it must be sorted by score, and contain brackets to handle all scores).
Video:How to replace nested IFs with VLOOKUP
21.

However, there are ways to overcome this limitation.
How can we look up both at once?
You want an exact match because there’s a chance that an order number won’t be found.

In this case, the exact match setting will cause VLOOKUP to return #N/A error.
Conversely, approximate matches are lightning fast because Excel is able to do what’s called abinary search.
The problem with binary searches however (i.e.

Worse, the result might look completely normal, so it can be very difficult to spot.
The solution is to use VLOOKUP twice, both times in approximate match mode.
The first instance simply checks that the value really exists.

Note: Your data must be sorted to use this trick.
It’s simply a way to protect against a missing lookup value while maintaining a fast lookup.
It’s a very powerful combination.

In straightforward situations, VLOOKUP will get the job done just fine with no fuss.
To learn more about INDEX and MATCH,see this article.